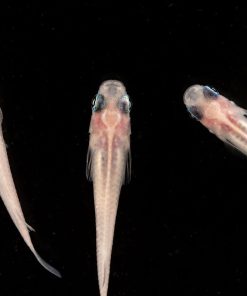
Leopard Cactus Pleco JA
$ 44,99 $ 26,99
L-Number: L114
Common Name: Leopard Cactus Pleco, Demini Leopard Cactus Pleco
Scientific Name: Pseudacanthicus cf. leopardus
Genus: Pseudacanthicus
Wild Origin: Brazil
Average Shipped Size: 1.5-1.9in
Adult Size: 10in
**Note: All livestock orders will come carefully packaged with solid wall Styrofoam insulation and shipped via 1-day shipping only. No extra insulation needs to be added to your cart for your livestock.
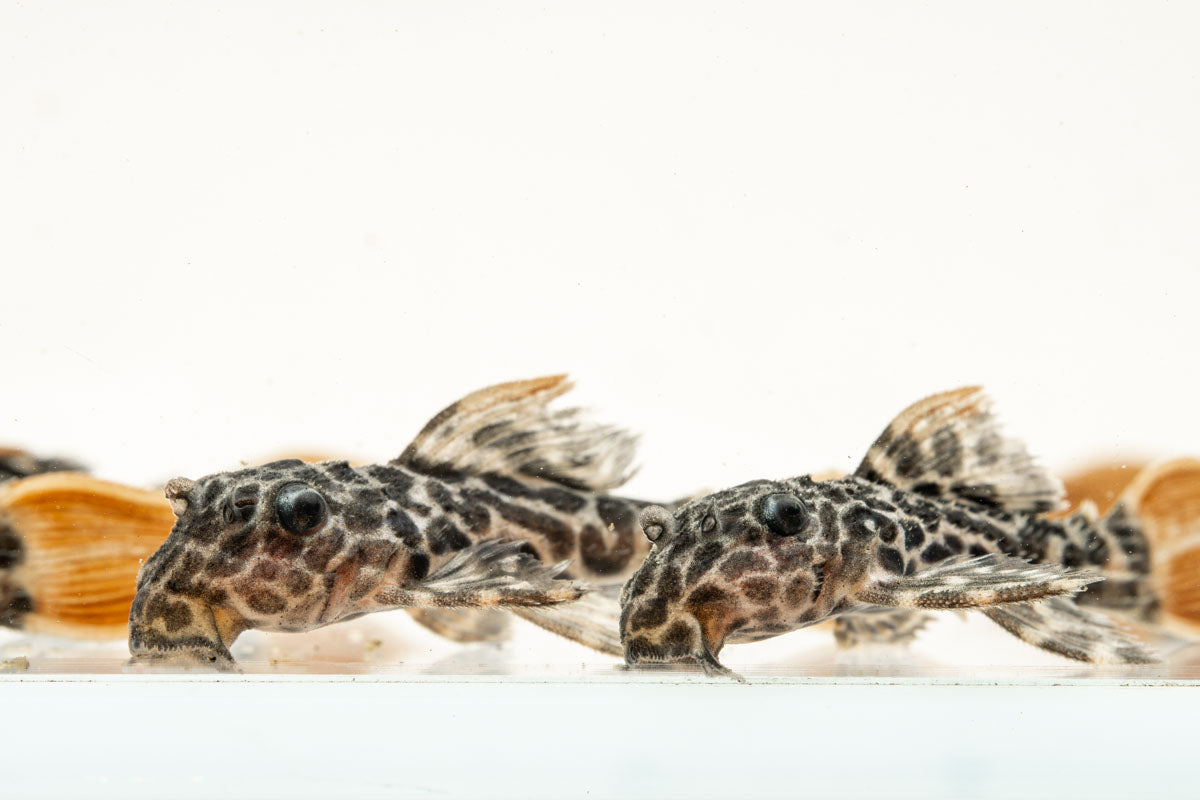
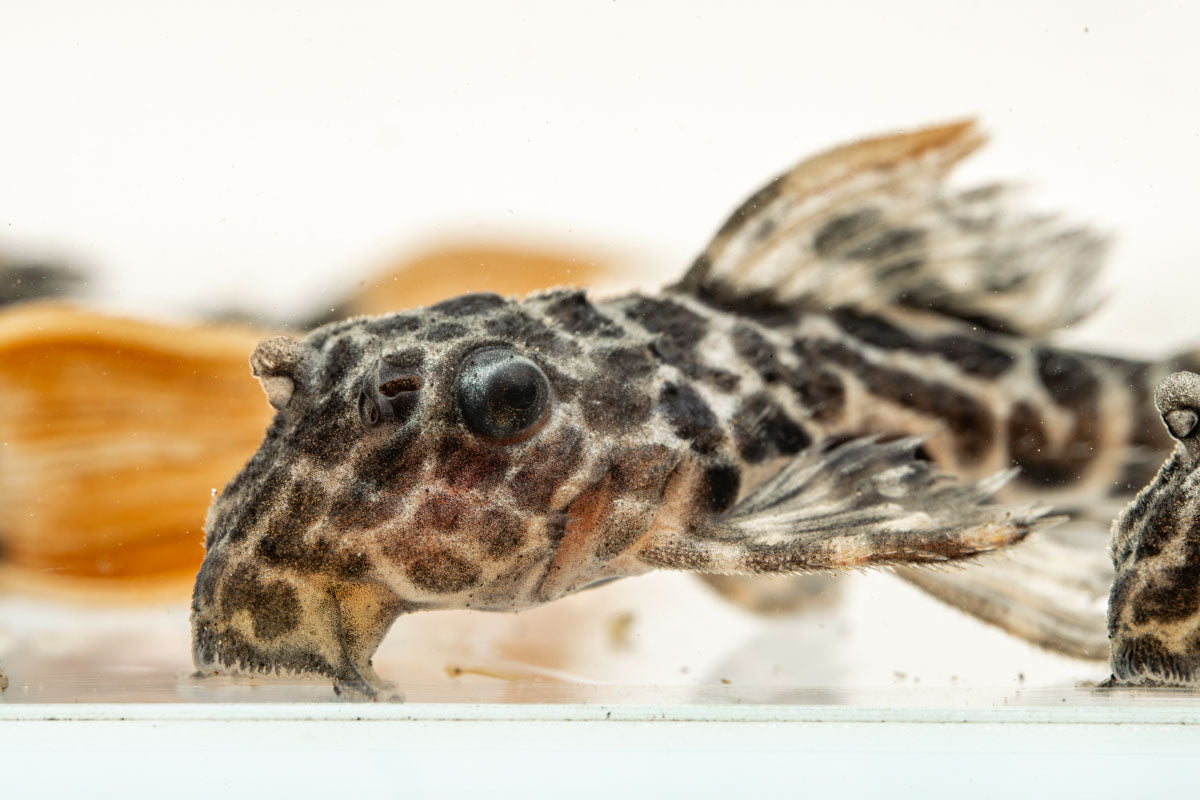
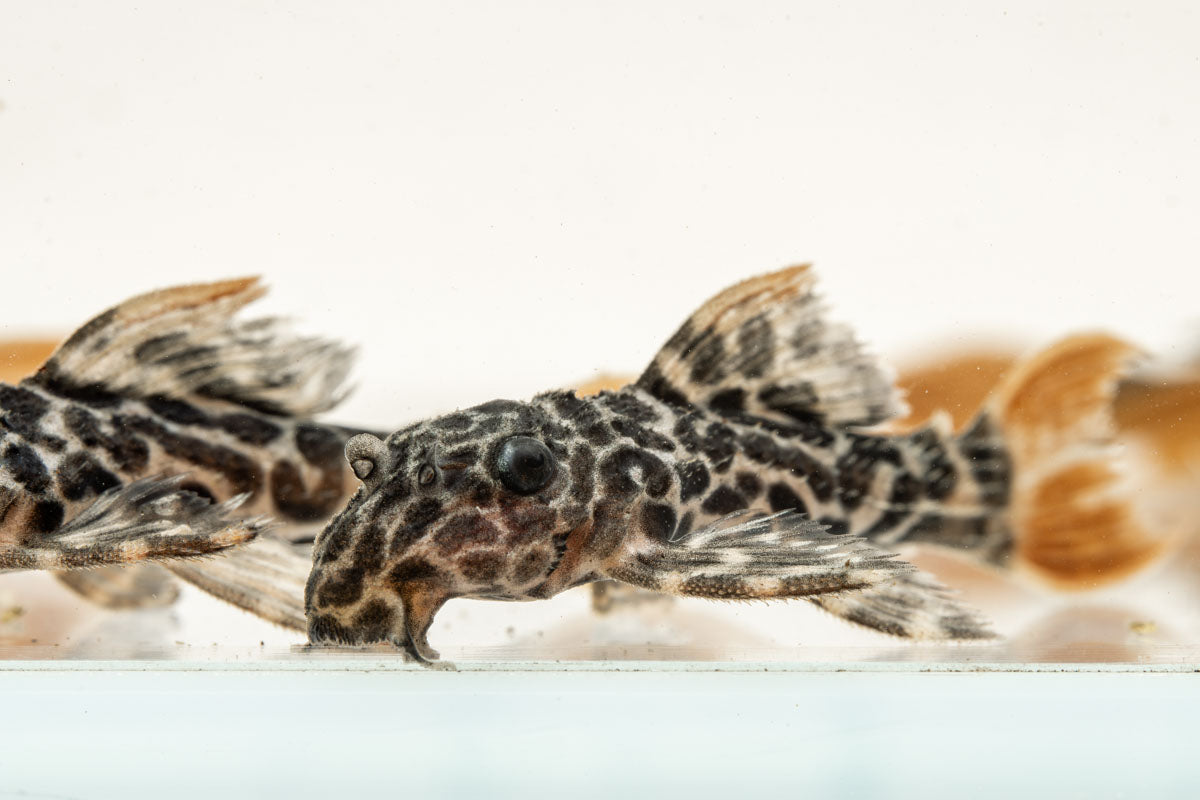
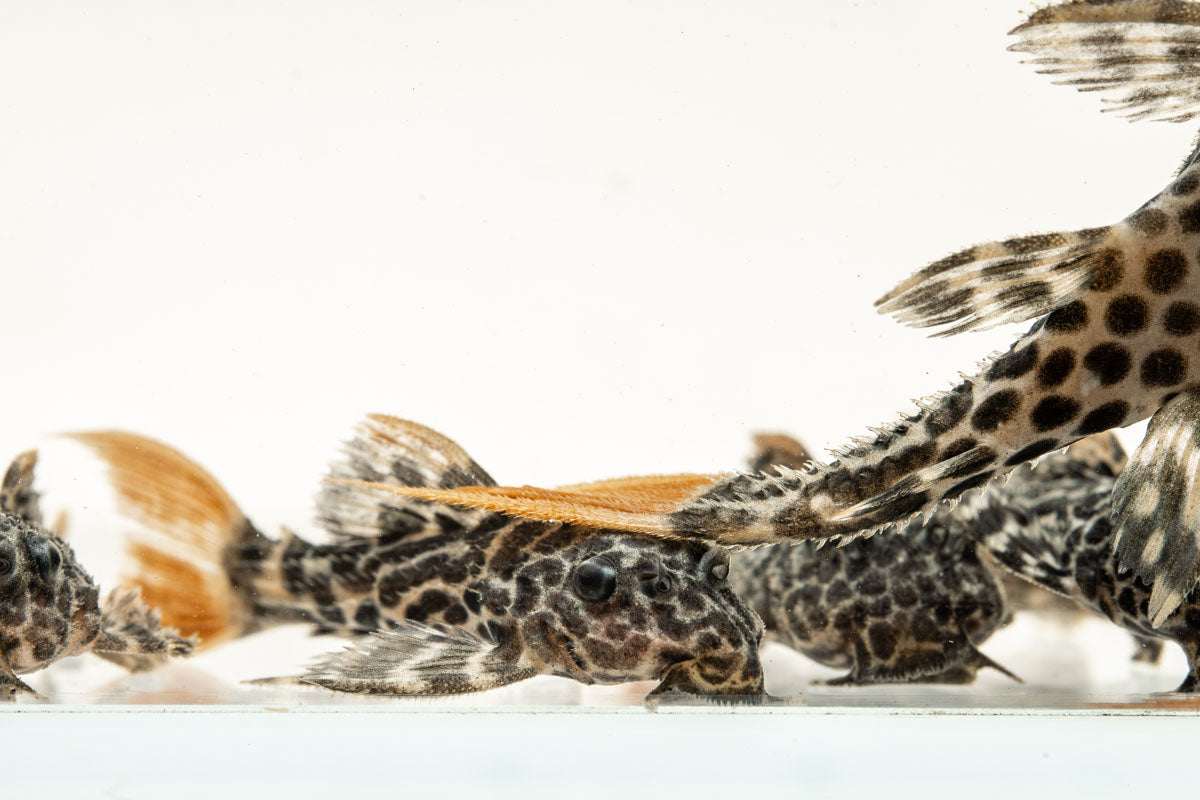
Found in a tributary of Brazil’s Rio Negro, the Leopard Cactus Pleco exhibits a distinct pattern featuring black spots against an orangish-brown body coloration, often likened to leopard spots. These plecos inhabit warm, acidic blackwater regions in their natural habitat. In aquariums, they are resilient and can adapt to a wide range of water parameters, but will do best in softer waters that emulate their natural habitat.
The Leopard Cactus Pleco is relatively peaceful, but may become territorial with similar species. As long as ample cover and hiding places are available, plecos do not generally bother other tankmates and make a great addition to mid-large sized community freshwater aquariums.
Key Features & Important Notes
- Unsexed juveniles
- Tank raised specimen
- Bright, bold pattern
- To increase survival rates, please allow 2-3 business days after an order is placed to properly prepare live animal shipments.
Recommended Water Parameters
Listed information should be treated as general guidelines only. We encourage you to do thorough research before committing to keeping any livestock.
- Temperature Range: 72-84°F
- pH: 6.5-7.5
- KH: 6-10
Recommended Tank Size
90 gallons. Tank size is relative and various factors should be considered when determining tank size. Factors include maintenance schedules, tank mates, desired colony size, and more.
Diet
Requires a mainly carnivorous diet. Feed meaty and high-protein foods like bloodworms or tubifex worms. Supplement with driftwood for biofilm-grazing. Commercially-available protein-rich foods like Repashy Gel Diets and Fluval Bug Bites will also be accepted.
Breeding
Juvenile Leopard Cactus Plecos are impossible to differentiate by sex, but as they mature, distinct gender characteristics emerge. Males develop prominent odontodes on their pectoral fins and heads, while females might have smaller, less noticeable ones. Females display rounder body shapes, while males possess broader, shorter heads. Full maturity might take up to 2 years, so patience is necessary if you’re looking to form breeding pairs from a group.
To prepare for breeding, ensure the adult breeders are well-conditioned with a diet of live and frozen foods beforehand. The simplest breeding method involves isolating a pair in a dedicated tank filled with ample caves. Pipes or plant pots make great make-shift “caves”. Cave entrances should be slightly larger than the fish so the female has enough room to lay her eggs. Maintain well-oxygenated water and keep the pH under 6.5. The spawning of the fish is induced by factors such as low air pressure and water changes.
The male picks a preferred spawning site and actively defends it. He entices the female to the site, though egg-laying might occur days later. Post-spawn, the female plays no further role and is chased away by the male. He handles parenting duties, safeguarding, and fanning the eggs with his fins. Once hatched, fry feed off their yolk sacs initially. Once consumed, provide newly hatched fry with algae wafers, baby brine shrimp, micro-worms, or crushed flakes.
| Size | Single, 3 Fish |
|---|
Fast Shipping with Professional Packaging
Our long-standing relationship with UPS FedEx DHL and other carriers around the world allows us to offer various shipping options. Our warehouse staff are highly trained to package your goods exactly as per the specifications we provide. Your goods are thoroughly checked and secured properly prior to shipping. We ship to hundreds of thousands of customers daily in different countries. The fact that we're dedicated to becoming the largest online retailer in the World is obvious. Warehouses and distribution centers are located in Europe as well as the USA.
Please note that orders with more than one item are subject to a processing period that is based to the specific item.
Before shipping, all ordered products will be thoroughly inspected. Most orders are shipped within 48 hours. The time to deliver varies from 3-7 days.
Returns
The stock is dynamic and we do not completely manage it because multiple stakeholders are involved, including our warehouse and factory. The stock can change at any moment. Be aware that your order will be unable to fill once you've placed your order.
Our policy runs for 30 days. If you don't receive your product within the 30 days period, we are not able to provide a refund or an exchange.
The item must not be used, and it must be in its original condition. The item must be in its original packaging.
Related products
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Terrestrial Plant
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Uncategorized
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Uncategorized
Fish
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant
Aquatic Plant